Introduction
Welcome to the Sympathetic Nervous System tutorial.
You will navigate through this tutorial using the buttons at the top of the screen.
The tutorial will ask you questions. Click on your chosen answer to see feedback; click the answer again to make the feedback disappear. When you're finished with one page, click the navigation button for the next page to move ahead.
Have fun! Click on button '1' to see the first page of the tutorial.
Page 1
Your sympathetic nervous system turns on when you are having an emergency. Which of the stimuli below would NOT make it turn on?
pain
Page 2
The Sympathetic Nervous System turns on automatically when you are under stress.
It turns OFF when you are relaxing or eating; so a stimulus like chocolate will reduce sympathetic system activity.
Eating turns on the opposite system, the PARASYMPATHETIC system. It's also called the 'rest and digest' system.
Page 3
The sympathetic System Response is also known as an ADRENALIN RUSH.This is because during the response, the adrenal medulla releases large amounts of adrenalin (also called epinephrine) into the blood.
A similar chemical, noradrenaline (also called norepinephrine) is released from the nerves of the Sympathetic System. (To remember it, just think 'nor' for nerves!)
Both of these chemicals have similar effects on the body. If you want to talk about both of them together, you call them the adrenergic neurotransmitters.
Page 4
Since you know the sympathetic system is for emergencies and the parasympathetic system is for relaxing, you should be able to sort the list of responses below. Click on the Sympathetic Responses - you should be able to find six.
Page 5
You can see from the list of Sympathetic System effects that this system can have very different effects on different cells, even though it sends the same neurotransmitters to each cell. Some cells speed up, some slow down.What could account for the different responses?
One answer is, the different cell surface receptors.
Page 6
The adrenergic neurotransmitters can attach to a wide variety of receptor molecules on the cell surface.These receptors were named 'alpha' and 'beta' receptors when they were first discovered.
As scientists looked at them more closely, they discovered that there were multiple kinds of alpha receptors and multiple kinds of beta receptors, so they subdivided them into alpha-1 and alpha-2, beta-1 and beta-2, and so on.
The more precisely we subdivide these receptors, the more control we gain as we develop drugs that will target just one receptor subtype.
Alpha-1 and beta-1 receptors are usually excitatory. They make tissues increase their activity. Which of these responses do you think will be caused by norepinephrine attaching to a beta-1 receptor?
Page 7
Your heart has beta-1 receptors, and when norepinephrine attaches to them the heart cells fire faster.Beta-1 receptors on other tissues can increase fat breakdown and help to increase metabolic rate. This gives you extra energy during the emergency.
Alpha-1 receptors are found in many different parts of the body, including the blood vessels, eyes, and skin. Which of the responses below is likely to happen when norepinephrine attaches to an alpha-1 receptor?
Page 8
Choose the right word to complete each sentence about what will happen when norepinephrine attaches to alpha-1 receptors.Alpha-1 receptors on the smooth muscles of blood vessels in the skin, guts, and kidneys will make the blood vessels constrict/ dilate.
When this happens in the skin, the person will turn flushed/ pale.
Alpha-1 receptors are also on the small muscles of the skin, attached to the hairs and surrounding the sweat glands. When norepinephrine attaches to them, these muscles will contract and cause warm, reddened skin/ cold, wet skin with goosepimples.
When blood vessels constrict in the kidneys, that will result in decreased urine production/ increased urine production.
When blood vessels in the guts constrict, the person may experience hunger/ nausea.
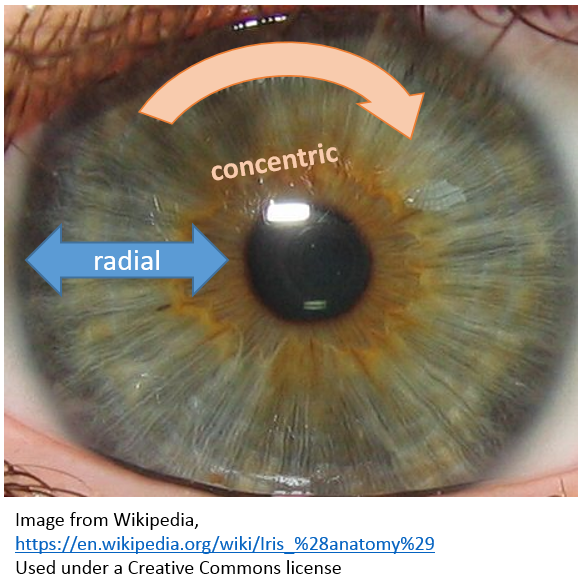 The radial muscles in your iris also contain alpha-1 receptors. When they constrict, the pupil will dilate/
constrict.
The radial muscles in your iris also contain alpha-1 receptors. When they constrict, the pupil will dilate/
constrict.
In addition to all this, the alpha-1 receptors excite smooth muscles in the sex organs. They're responsible for ejaculation.
Page 9
Alpha-2 and beta-2 receptors tend to cause the cells they are on to decrease function.
Alpha-2 receptors are the ones that turn off the digestive tract during an emergency. They decrease insulin release from the pancreas, causing blood glucose levels to go up.
They also are found on the cells that release norepinephrine. When the alpha-2 receptors on these cells are stimulated, they inhibit further norepinephrine release.
What would you call this type of response?
Page 10
Beta-2 receptors tend to relax smooth muscles.You find them in your airways: one way to remember this is that you have 2 lungs, so they contain Beta-2 receptors. In the lungs, the Beta-2 receptors cause the bronchioles to dilate, making it easier for you to breathe.
Beta-2 receptors also make your liver release glucose into the blood and make your muscle cells break the glucose down for energy. They dilate the blood vessels in your skeletal muscles so the muscle cells can get plenty of food and O2. When you hear of people having 'superhuman strength' in an emergency, a lot of it is due to Beta-2 receptors!
Page 11
This is the end of the Sympathetic Nervous System review! Here's a summary of what you've learned so far.
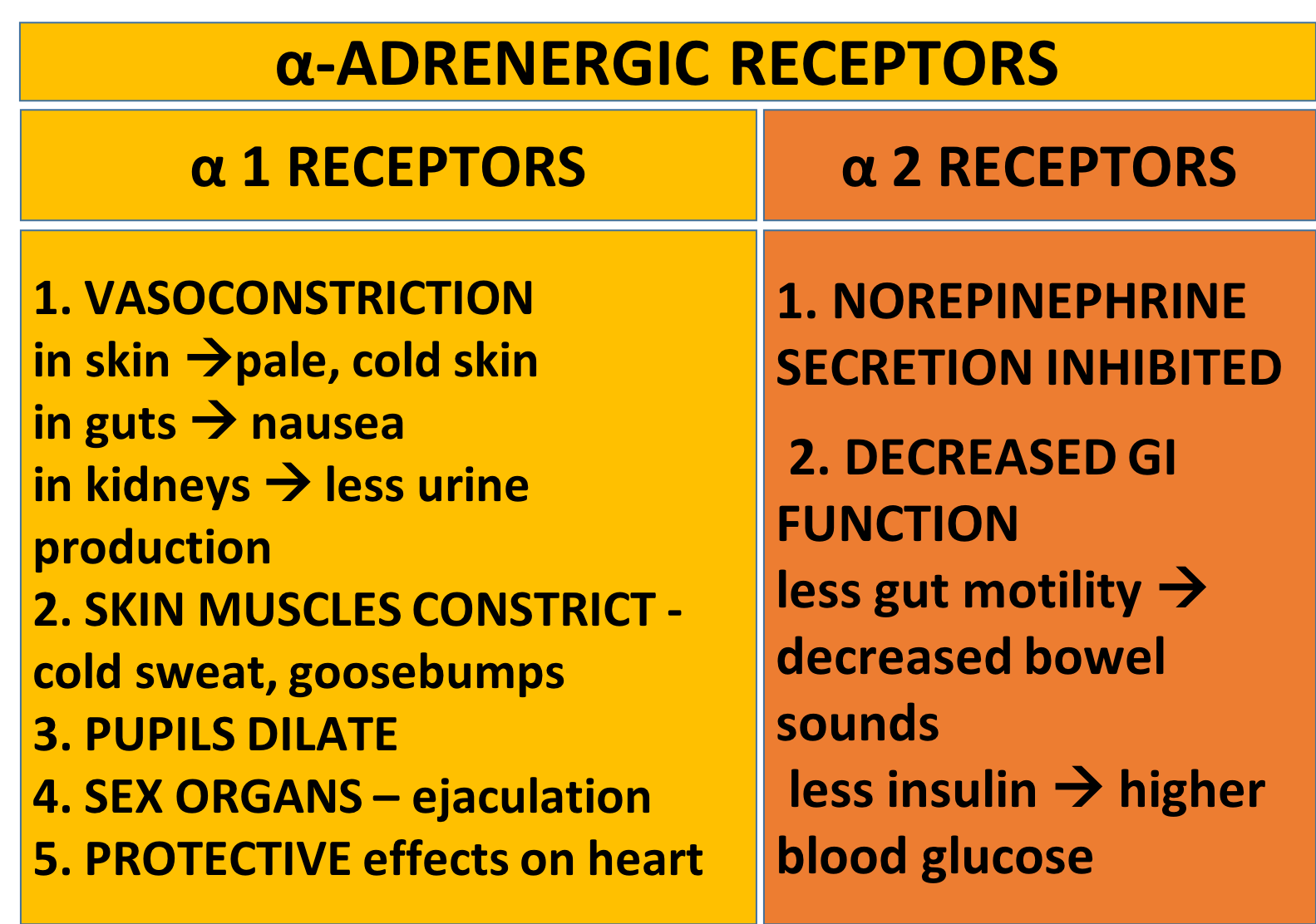
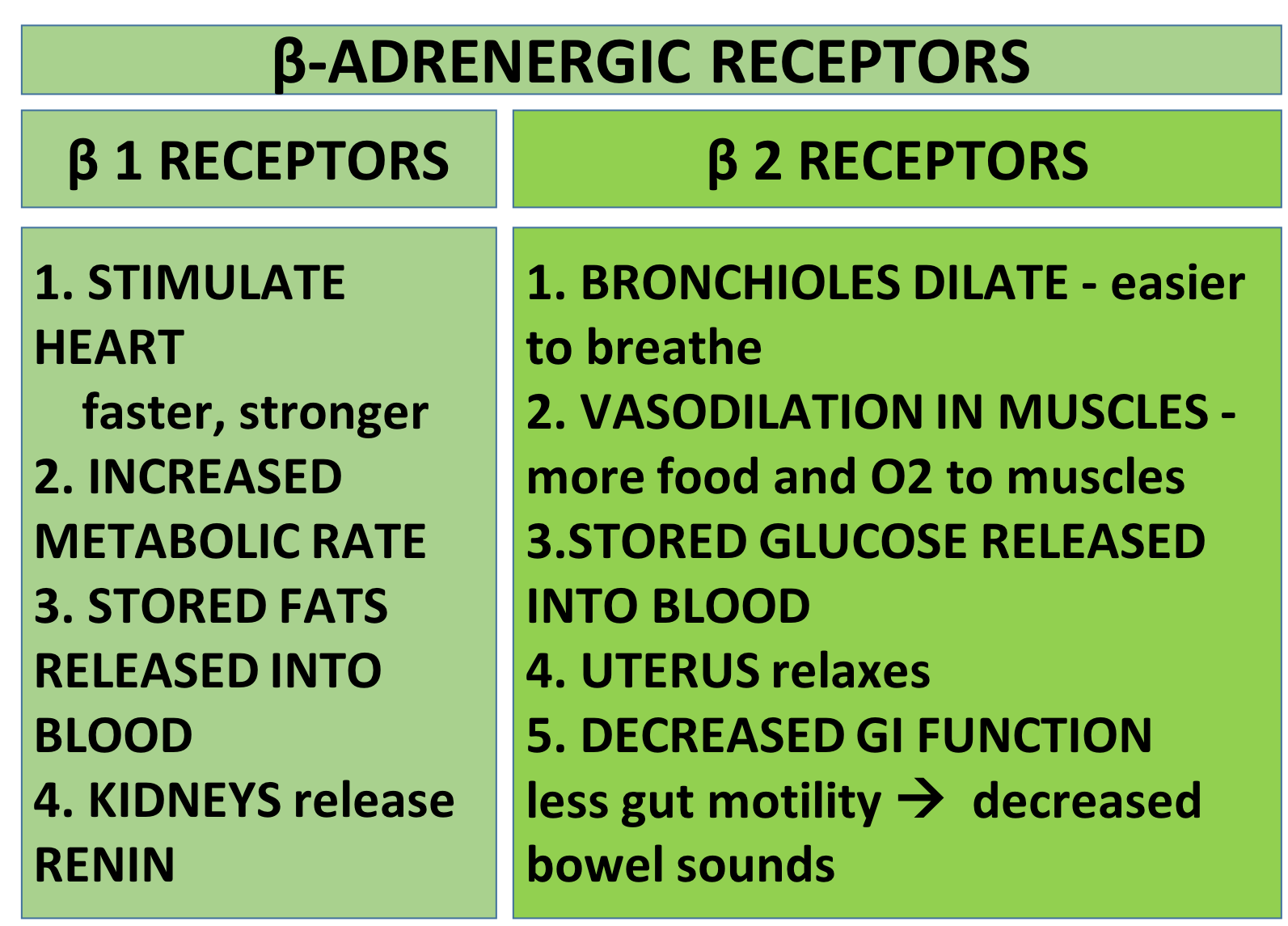
Now you should be able to explain some case studies.
Page 12
Try to predict what will happen to each of these patients. When you think you've got it, click on the patient to see the answer.That's it for this tutorial! I hope you feel confident with the basics of the Sympathetic Nervous System and how it affects body function.
This is just one of the responses your body uses to handle stress. The others are the Corticotropin Releasing Hormone System, the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System, and Antidiuretic Hormone. You can reach them by clicking on their names.
Material for this activity is taken from:
Fox, S.I. (2013) Human Physiology, 13th ed., McGraw-Hill
Seeley, R., VanPutte, C., Regan, J. and A. Russo (2011) Seeley's Anatomy and Physiology, 9th ed. McGraw-Hill