Introduction
This tutorial will take you through a case history of a woman with GI problems.
You will navigate through this tutorial using the buttons at the top of the screen.
The tutorial will ask you questions. Click on your chosen answer to see feedback; click the answer again to make the feedback disappear. When you're finished with one page, click the navigation button for the next page to move ahead.
Have fun! Click on button '1' to see the first page of the tutorial.
Page 1
Ms. P is a forty-three year old caucasian female, 5'6" and 184 pounds, with a history of GI discomfort, especially after meals.
She had lost five pounds in the past month and says she wouldn't complain about this at all, except that she has such bad gas and her stools smell foul, and her stomach hurts whenever she eats. She describes upper right quadrant pain after every meal, sometimes but not always relieved by antacids.
Her doctor makes a provisional diagnosis of malabsorbtion syndrome.
What could malabsorbtion cause?
Page 2
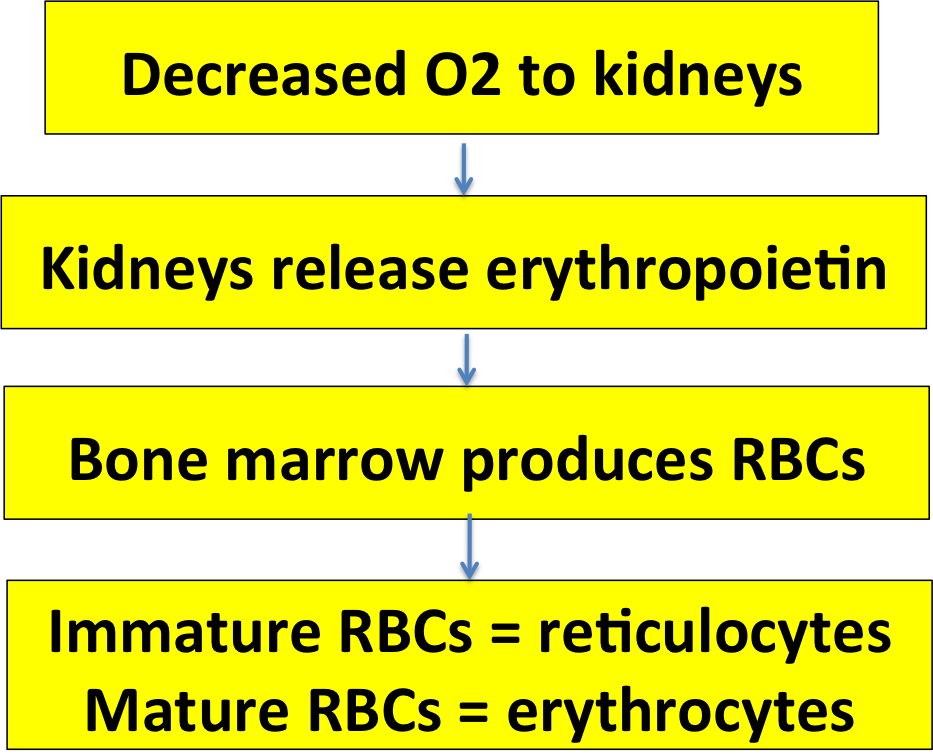
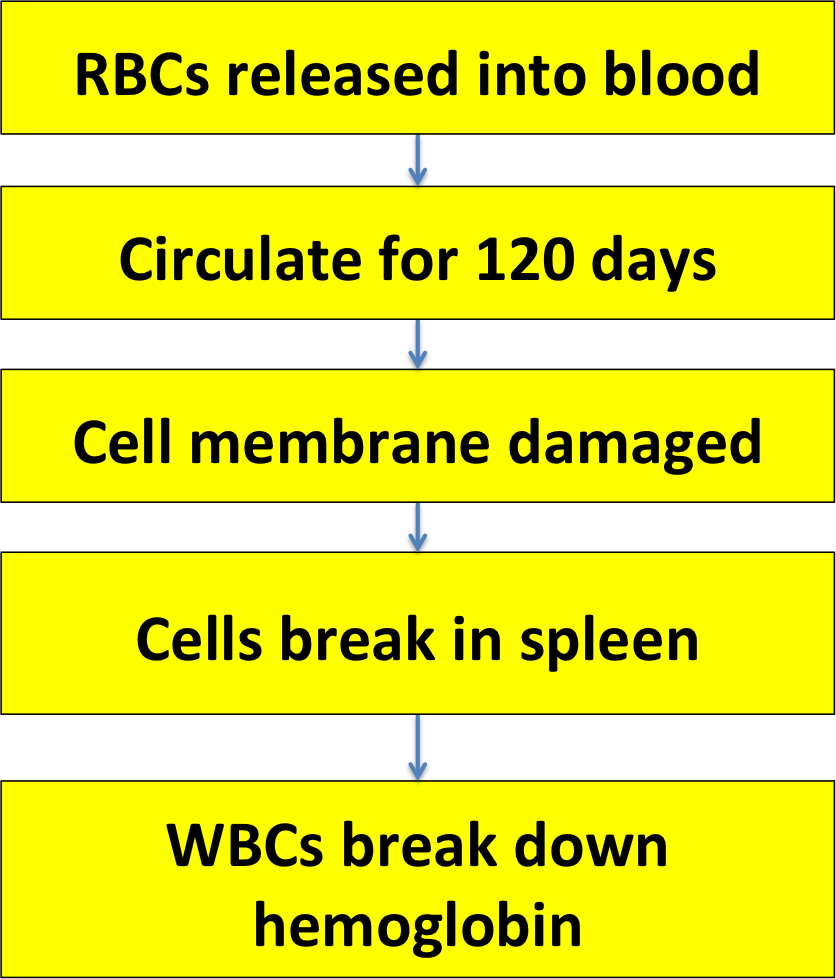
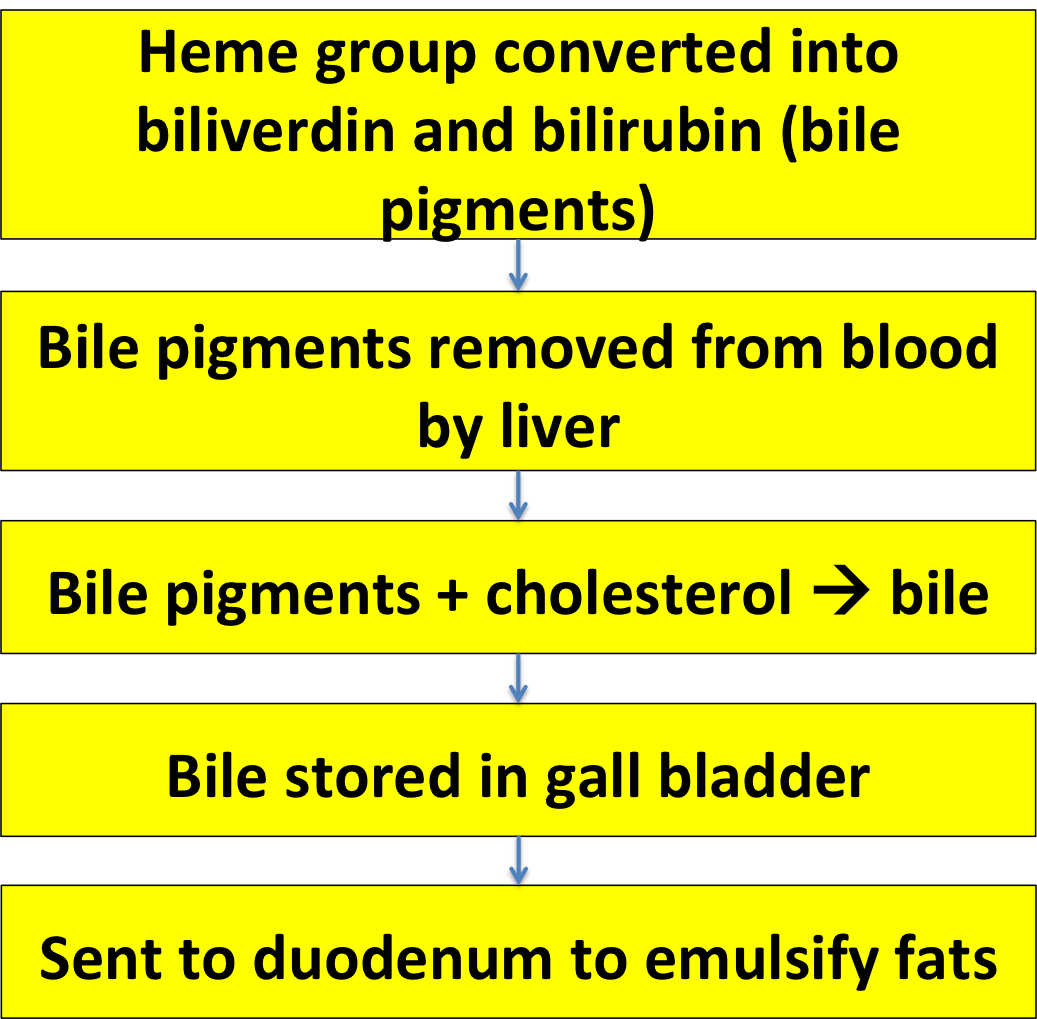
Here's a flow chart you should recognize, showing how RBCs are made in the bone marrow, released into the blood, and destroyed by the spleen when they wear out.
When the RBCs are destroyed in the spleen the hemoglobin inside them is converted to bilirubin and biliverdin.
These compounds can cause the skin to turn yellow (jaundice) - except that they're usually removed by the liver and made into bile. The bile is stored in the gall bladder and then sent to the duodenum to help emulsify fats so they can be digested.
How does this relate to Ms. P? Well, the reason for Ms. P's malabsorbtion wasn't initially clear, but then she began to develop a yellowish coloration in her skin and sclerae. What is the most likely cause of her problems?
Page 3
The doctor has ordered several tests. Alanine aminotransferase levels (ALT) and plasma protein levels are normal. What do these tests tell you?Page 4
The liver seems to be working all right, so Ms. P's jaundice must be due to something else. The doctor thinks it might be obstruction of the bile duct, so a fecal urobilinogen test is ordered.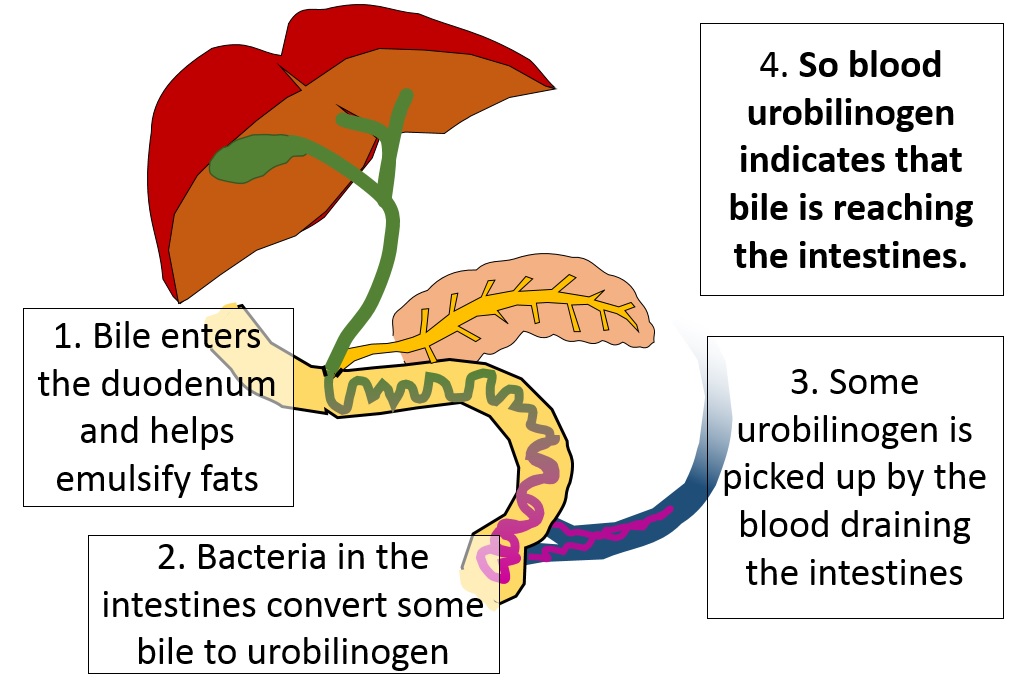
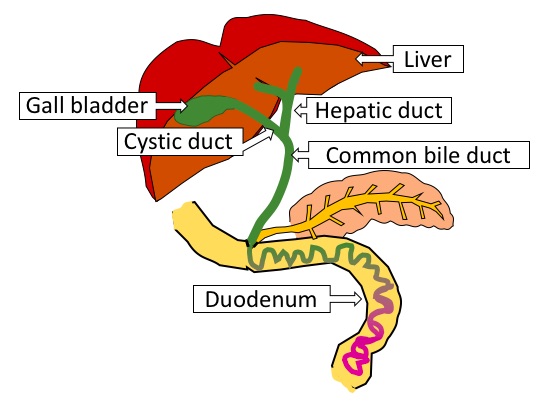
In this image, you can see the bile going from the liver and gall bladder down the common bile duct
into the duodenum. In the intestines, some of the bile is converted to urobilinogen, which can
then pass on down the bowel into the feces.
Some of the urobilinogen will be reabsorbed from the intestines along with food; that means it can get into the blood and the urine, so the doctor could measure it there as well. But it's only made when bile is in the intestines.
What will the results of the fecal urobilinogen test be, if the bile duct is obstructed?
Page 5
Ms. P has low fecal urobilinogen, indicating that bile is not entering her intestines. She also reports more episodes of pain after eating.The doctor has ordered cholecystography to check for gallstones, and says the pain after eating could be either an inflamed gallbladder (cholecystitis) or biliary colic. Ms. P wants to know how gallstones would cause colic.
by stretching the cystic duct or common bile duct
by stretching the hepatic duct
The night before her cholecystography Ms. P arrives in the Emergency Department, acutely ill. She complains of severe abdominal pain when lying down, relieved when she sits up. The pain is now in the left upper quadrant rather than the right. Her abdomen is distended, bowel sounds are decreased, and her blood pressure is 90/50 mm Hg with cool, clammy skin, restlessness, and a heart rate of 115 bpm.
What complication does she seem to be developing?
encephalitis (brain inflammation)
ARDS (acute respiratory distress syndrome
Page 6
Now the problem is to figure out why this happened. A new set of tests are ordered -- and they reveal that her serum amylase, serum lipase, and blood glucose are all elevated.What do these tests tell you?
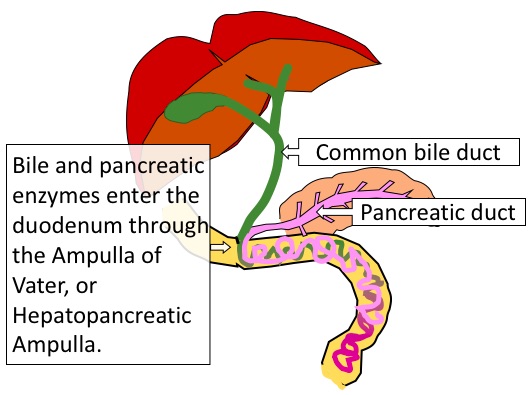
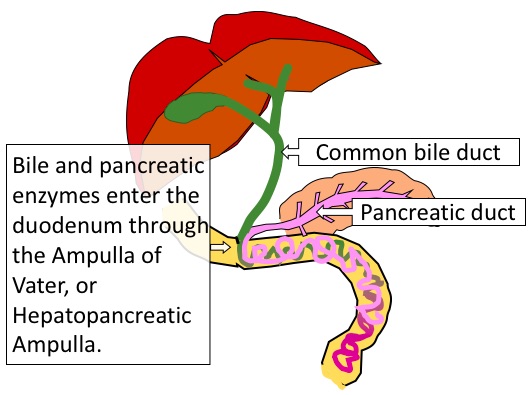
Let's look at the biliary tract again. Last time, we were focused on how bile flows down the
common bile duct into the duodenum. But now, let's look at how enzymes like lipase and amylase move into the duodenum
from the exocrine pancreas.
In this diagram, you can see that the exocrine pancreas has a duct - the pancreatic duct
- which joins the common bile duct to form a little nozzle called the
ampulla of Vater (also called the duodenal papilla, because it empties into the duodenum,
or the hepatopancreatic ampulla, because it is carrying secretions from both the liver and
the exocrine pancreas).
The tip of the duct has a sphincter muscle called the sphincter of Oddi, which can open
or close to control whether bile and enzymes flow into the duodenum.
The pancreatic enzymes amylase and lipase should be flowing down the pancreatic duct into the ampulla of Vater and into the duodenum. But instead, the tests reveal that these enzymes are in the blood! How could that happen?
she could have a tumor in her salivary glands
Page 7
The lipase and amylase in Ms. P's blood indicate damage to her pancreas cells, and so could her elevated blood glucose. Which parts of the pancreas might be damaged?Page 8
The doctor thinks Ms. P has pancreatitis, which is affecting both her exocrine pancreas (causing elevated amylase and lipase) and her endocrine pancreas (causing decreased insulin secretion and elevated blood glucose).
What type of pancreatitis do you think she has?
But how could her previous problems be related to this? Let's look at the biliary tract again.
The doctor suspected a gallstone was blocking the bile duct, because she reported signs similar to biliary colic, pain caused when the gallsone passes down the cystic and comon bile ducts. In fact, she would have been tested for gallstones if this emergency hadn't come up. Could a gallstone be causing her pancreas problems too?
Page 9
The only way a gallstone could affect pancreas secretion is if it slid down the common bile duct all the way to the ampulla of Vater and blocked that.
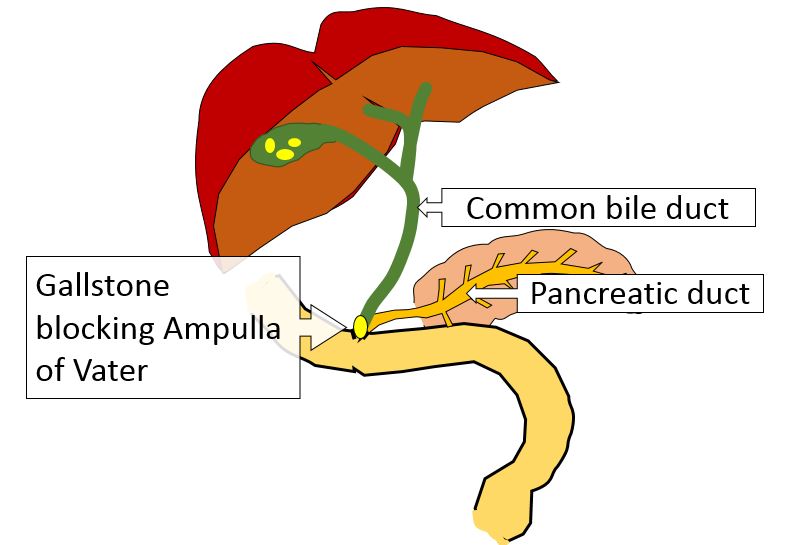
The gallstone in the ampulla of Vater is preventing pancreatic enzymes and bile from reaching the duodenum. But more is happening!
The gallbladder is a muscular organ. When you eat fat and your duodenum releases cholecystokinin, the gallbladder squeezes and squirts bile into the duodenum. If the ampulla of Vater is blocked, though, where will that bile go?
There's only one place it can go - up the pancreatic duct, into the pancreas.
Page 10
This is called biliary reflux, and it causes a lot of problems. Inside the pancreas, the bile disrupts the walls of the pancreatic duct. It also activates the digestive enzymes that the pancreas has been emptying into that duct.

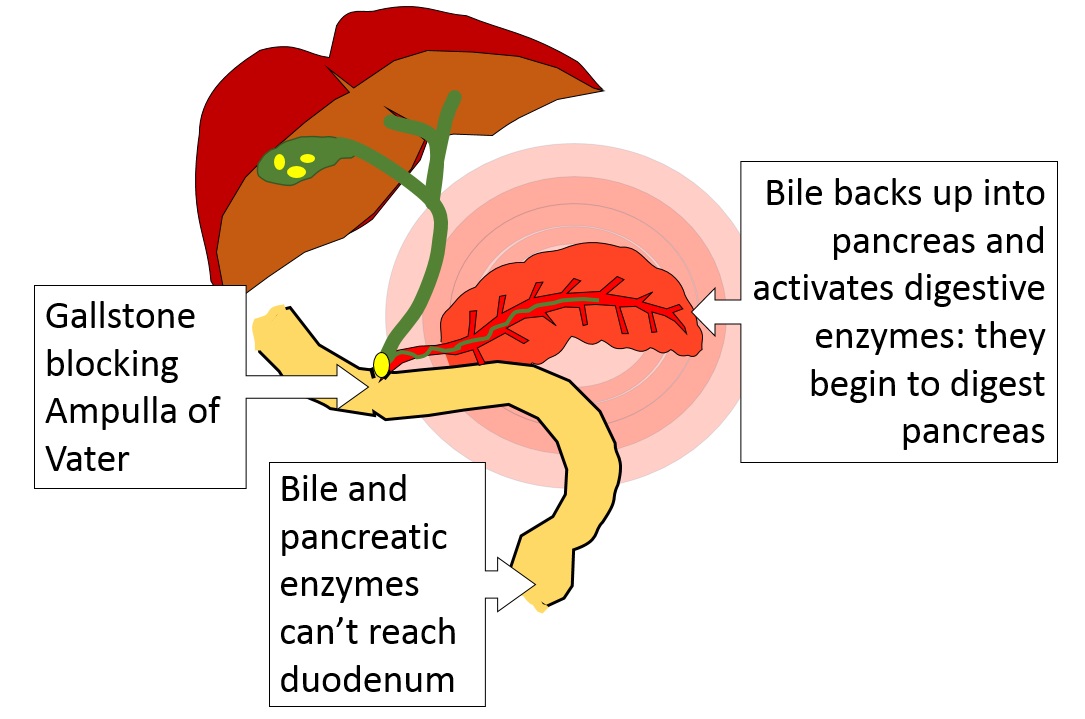
This is called autodigestion and it is both painful and dangerous!
Pancreas review page 1
Scattered through the pancreas are small groups of cells which aren't attached to the ducts. They lie between the lobules. These groups of cells make up the endocrine pancreas - they have no ducts, but their secretions go directly into the bloodstream and are carried throughout the body.
Pancreas review page 2
Pancreas review page 3
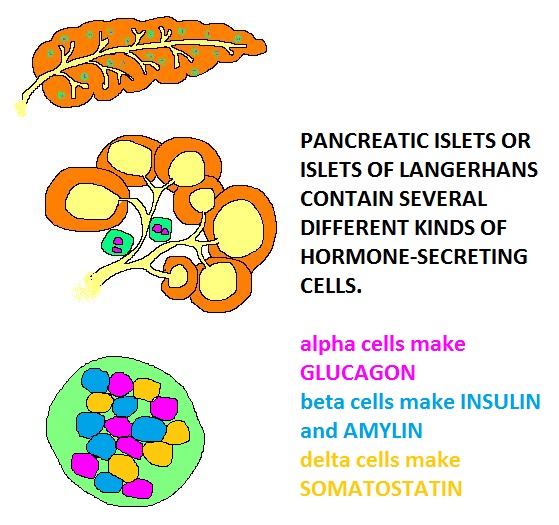

GLUCAGON is the easiest of the endocrine pancreas hormones to remember, because you make it when your blood GLUcose is GONe.
Low blood glucose causes the alpha cells to release GLUCAGON into the blood, and GLUCAGON causes the cells in your body to break down their stored foods and release them into the blood for other cells to use. Stored glycogen is broken into glucose, stored fat is broken into free fatty acids, and stored protein is broken into amino acids. This is the hormone that makes you lose weight when you go on a diet!
When the blood glucose has increased to a normal level, the alpha cells will no longer be stimulated to release glucagon, and the glucagon levels will decrease.
This is a classic negative feedback loop, keeping blood glucose levels from dropping too low. But what if your blood glucose increased - for instance, if you ate a lot of sugar?
Pancreas review page 4

While there's always some insulin produced, high blood glucose causes the beta cells to release more. The increased insulin makes your cells take up food faster, so the food you just ate gets picked up and stored as glycogen, fats, or proteins.
When the food has been stored by the cells and blood glucose goes back down to normal, the insulin secretion will also go back down to normal.
Pancreas review page 5
In summary, the exocrine pancreas delivers enzymes to the duodenum through a duct, while the endocrine pancreas creates insulin and glucagon to regulate blood glucose levels. Glucagon raises blood glucose levels, while insulin lowers them by making cells pick up food from the blood and store it.
Now how does this relate to Ms. P's problems? Go to page 7 of the main tutorial to apply what you've just reviewed.
Page 11
As pancreatic cells are destroyed and blood vessels inside the pancreas broken open, pancreatic enzymes enter the blood.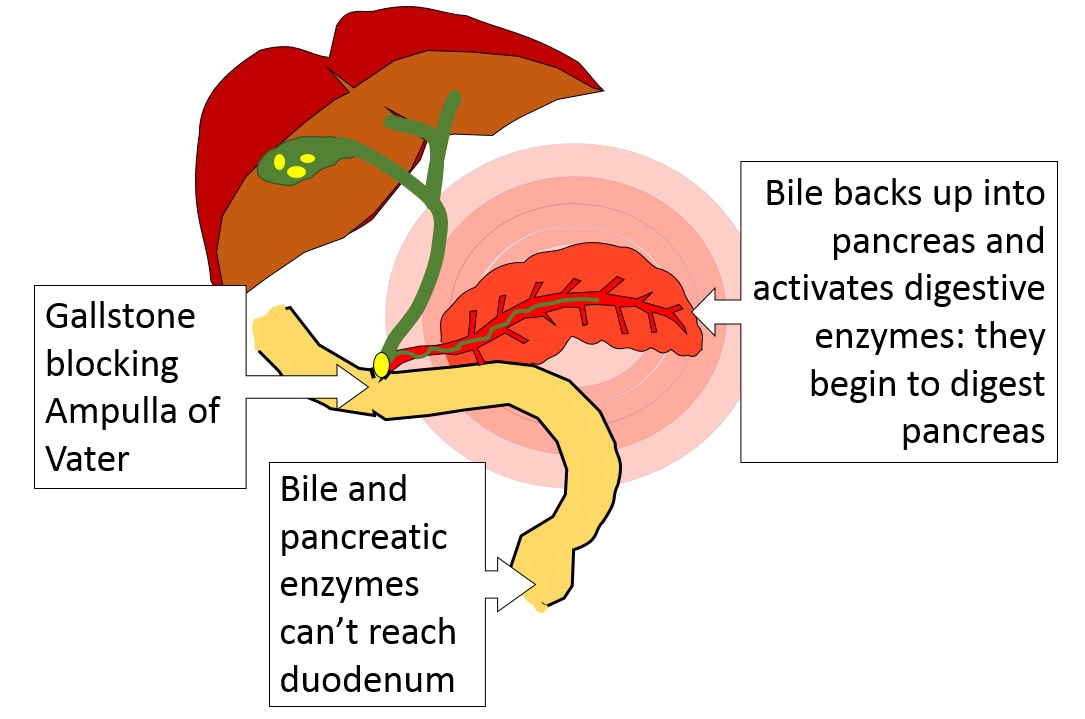
Let's look at her presentation again. Which parts of it could be caused by her pancreatic inflammation? Click on the ones you think are correct.
She complains of severe abdominal pain when lying down, relieved when she sits up. Her abdomen is distended, bowel sounds are decreased, and her blood pressure is 90/50 mm Hg with cool, clammy skin, restlessness, and a heart rate of 115 bpm.
Page 12
Ms. P is suffering pain and abdominal distension due to the inflammation in her pancreas. Which of her signs and symptoms are due to the generalized stress response activated by the pain?
She complains of severe abdominal pain when lying down, relieved when she sits up. Her abdomen is distended, bowel sounds are decreased, and her blood pressure is 90/50 mm Hg with cool, clammy skin, restlessness, and a heart rate of 115 bpm.
Page 13
Ms. P was diagnosed with acute pancreatitis caused by gallstones and biliary reflux. She was kept on an isotonic IV to stabilize blood pressure, and the afternoon after her arrival at the ER, surgeons performd an endoscopic sphincterectomy. They passed an endoscope down her GI tract into the duodenum, cut the sphincter of Oddi, removed the gallstone from the ampulla, and inserted a stent to keep the ampulla from swelling shut.This restored the free flow of bile and pancreatic enzymes into her duodenum.

The gallbladder contains stones
The gallbladder may pass another stone and cause another blockage of the ampulla.
Why was she directed to eat a low-fat diet?
To decrease the workload on the pancreas
Material for this activity is taken from:
Greenspan, F. S., and D. G. Gardner, 2004. Basic & Clinical Endocrinology, seventh edition. McGraw
Hill Publishers.
Seeley, R.R. , Stephens, T.D., and P. Tate, 2003.Anatomy and Physiology, 6th Edition. McGraw-Hill Higher Education.